Office Fabric UI - React/Redux (Part 1 of 5)
This post will go over creating a SharePoint Hosted Add-In using the Office Fabric UI React framework and Redux. It’s a continuation of a previous post, but we will now incorporate Redux. I’ve broken this post into five parts: 1. Introduction and Project Creation (This Post) 2. Core Configuration/Files 3. Office UI Fabric Dialog 4. Office UI Fabric Panel 5. Office UI Fabric Details List
The entire project is on github.
Updated Jan 2018
I’ve updated this post to use the latest versions of the libraries from Jan 2018.
Updated For WebPack 2.0
I’ve updated this post to fix the issues with webpack.
Redux
Redux helps with complex applications, where different independent components of the solution need to interact with the same data.
Core Principals
-
One immutable store
- All application states are stored here.
- Immutable - can’t be changed.
- State - A dynamic object that is referenced by various components in the application.
-
Actions trigger changes
- Events that trigger state value changes.
-
Reducers update state
- Pure functions that accept the current state from an action and returns a new state.
Flow
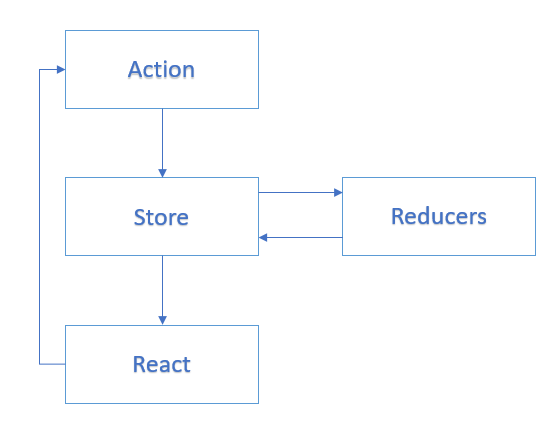
Store
The store contains the immutable states of the components.
Reducers
Reducers accept the data from an action and create a new “state”, since the store is immutable.
Action
Actions define the available events of the component. These are generally the DOM events or CRUD operations of the application.
React
The store will send the state changes to “React” which will handle the requested actions.
Project Setup
Since this is a continuation of a previous post, I will not go into details of the basic configuration and assume that you have a basic knowledge of the required components and how to use them. If you do not feel comfortable, please read the previous post before moving forward with this one.
Required Software
NPM Package Configuration
First thing we will do is create the project. Using the command prompt, create an empty project folder where you want to create the project in.
Create the package.json file
npm init --y
Note - The –y option will default the values.
Install the dependencies
npm i --save office-ui-fabric-react react react-dom redux redux-thunk react-redux
- gd-sprest - Library used to execute requests against the SharePoint REST API.
- office-ui-fabric-react - Microsoft Office Fabric UI React library
- react - React library
- react-dom - React DOM library (Required for React)
- redux - Redux library
- redux-thunk - Redux plugin for asynchronous actions
- react-redux - React plugin for Redux. Note - Use redux-saga instead of redux-thunk. This library is recommended for people new to React/Redux.
Install the development dependencies
npm i --save-dev @types/react @types/react-dom babel-core babel-preset-es2015 babel-preset-react react-hot-loader ts-loader webpack
- @types/react - Required to compile the react code.
- @types/react-dom - Required to compile the react code.
- babel-core - Required to use “Babel”
- babel-loader - Compiles the JSX code to JavaScript.
- babel-preset-es2015 - Converts the JavaScript to ES2015 (The current web standard supported by browsers)
- react-hot-loader - Plugin for the webpack development server for hot reloading.
- ts-loader - Compiles the TypeScript code to JSX.
- webpack - Used to compile, bundle and minify the source code.
Update the package.json
Below is the package configuration file. The “dependencies” and “devDependencies” properties are updated by running the npm install commands in the previous sections. The part to add is the “scripts” property to build and test the solution. Reference the “webpack.config.js” section for additional information.
{
"name": "gd.fabric-redux.ux",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "GD.FabricRedux.UX",
"main": "src/index.tsx",
"author": {
"name": "Gunjan Datta"
},
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack",
"test": "webpack-dev-server --hot --inline --colors --progress"
},
"dependencies": {
"gd-sprest": "^2.5.9",
"office-ui-fabric-react": "^5.38.0",
"react": "^16.2.0",
"react-dom": "^16.2.0",
"react-redux": "^5.0.6",
"redux": "^3.7.2",
"redux-thunk": "^2.2.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/react": "^16.0.34",
"@types/react-dom": "^16.0.3",
"babel-core": "^6.26.0",
"babel-loader": "^7.1.2",
"babel-preset-es2015": "^6.24.1",
"babel-preset-react": "^6.24.1",
"es6-promise": "^4.2.2",
"object-assign": "^4.1.1",
"react-hot-loader": "^3.1.3",
"ts-loader": "^3.2.0",
"webpack": "^3.10.0"
}
}
tsconfig.json
Below is the typescript configuration file. These options will do the following:
- Compile the react code
- Target ES5 code standards
{
"compilerOptions": {
"jsx": "react",
"target": "es5"
}
}
Create the webpack.config.js file
Below is the webpack configuration file. It contains all the information to compile and bundle the source code.
var path = require('path');
module.exports = {
// Target the output of the typescript compiler
context: path.join(__dirname, "src"),
// File(s) to target
entry: './index.tsx',
// Output
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
publicPath: "/dist/"
},
// Resolve the file extensions
resolve: {
extensions: [".js", ".jsx", ".ts", ".tsx"]
},
// Module to define what libraries with the compiler
module: {
// Rules
rules: [
{
// Target the .ts and .tsx files
test: /\.tsx?$/,
// Exclude the node modules folder
exclude: /node_modules/,
// Define the compiler to use
use: [
{
// Compile the JSX code to javascript
loader: "babel-loader",
// Options
options: {
// Ensure the javascript works in legacy browsers
presets: ["es2015"]
}
},
{
// Compile the typescript code to JSX
loader: "ts-loader"
}
]
}
]
}
};
Conclusion
This ends part one of the blog post. The next post will go over the core file and folder structure of the application.