SharePoint 2013 Modern WebPart (3 of 4)
- Modern WebPart Overview
- Demo 1 - TypeScript
- Demo 2 - React
- Demo 3 - VueJS (This Post)
- Demo 4 - AngularJS
VueJS WebPart Example
This is the third of four demos giving an overview of creating modern webpart solutions for SharePoint 2013+ environments. The demo code can be found in github. The goal of this post is to give an example of using VueJS, while expanding on the previous post. This is the first time I’ve coded in VueJS, so this should be fun.
Requirements
- NodeJS - A superset of JavaScript functions. NodeJS allows us to develop code similar to C#, which is compiled into JavaScript.
Create the Project
There is a vue-cli to help create projects, which is very useful, but for this demo I want to do the absolute minimal amount of things to compile the project.
mkdir demo-wp-vuejs
cd demo-wp-vuejs
npm i --y
I selected ‘no’ to all questions and selected ‘npm’ to install after the wizard completes.
Install Libraries
- gd-sprest - The library used to create the webpart
-
VueJS - The VueJS library
- css-loader is required for compiling the css to JavaScript
- vue-loader - Used to compile the VueJS code to JavaScript
- vue-template-compiler - Since the sample code is using a template, we will need to include this library
npm i --save gd-sprest gd-sprest-js vue
npm i --save-dev core-js css-loader style-loader vue-loader vue-template-compiler webpack webpack-cli
Source Code
Create a “src” folder and add the following files
SharePoint Configuration (src/cfg.ts)
This configuration file splits out the list and webpart configurations.
import { $REST } from "gd-sprest";
/**
* Configuration
*/
export const Configuration = {
// List
List: $REST.Helper.SPConfig({
ListCfg: [{
CustomFields: [
{
choices: ["Business", "Family", "Personal"],
name: "MCCategory",
type: $REST.Helper.SPCfgFieldType.Choice
},
{
name: "MCPhoneNumber",
type: $REST.Helper.SPCfgFieldType.Text
}
],
ListInformation: {
BaseTemplate: $REST.SPTypes.ListTemplateType.GenericList,
Title: "My Contacts"
},
ViewInformation: [
{
ViewName: "All Items",
ViewFields: ["MCCategory", "LinkTitle", "MCPhoneNumber"],
ViewQuery: "<OrderBy><FieldRef Name='MCCategory' /><FieldRef Name='Title' /></OrderBy>"
}
]
}]
}),
// WebPart
WebPart: $REST.Helper.SPConfig({
WebPartCfg: [
{
FileName: "wpContacts_vuejs.webpart",
Group: "Demo",
XML: `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<webParts>
<webPart xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/WebPart/v3">
<metaData>
<type name="Microsoft.SharePoint.WebPartPages.ScriptEditorWebPart, Microsoft.SharePoint, Version=15.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=71e9bce111e9429c" />
<importErrorMessage>$Resources:core,ImportantErrorMessage;</importErrorMessage>
</metaData>
<data>
<properties>
<property name="Title" type="string">My Contacts (VueJS)</property>
<property name="Description" type="string">Demo displaying my contacts.</property>
<property name="ChromeType" type="chrometype">TitleOnly</property>
<property name="Content" type="string">
<script type="text/javascript" src="/sites/dev/siteassets/demo-vue.js"></script>
<div id="wp-vuejs"></div>
<div id="wp-vuejs-cfg" style="display:none;"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">SP.SOD.executeOrDelayUntilScriptLoaded(function() { VueJSDemo.init(); }, 'demo-vue.js');</script>
</property>
</properties>
</data>
</webPart>
</webParts>`
}
]
})
};
// Create the test data function
Configuration.List["createTestData"] = () => {
// Test Data
let data = [
{
MCCategory: "Business",
MCPhoneNumber: "111-111-1111",
Title: "John A. Doe"
},
{
MCCategory: "Business",
MCPhoneNumber: "222-222-2222",
Title: "John B. Doe"
},
{
MCCategory: "Family",
MCPhoneNumber: "333-333-3333",
Title: "John C. Doe"
},
{
MCCategory: "Family",
MCPhoneNumber: "444-444-4444",
Title: "John D. Doe"
},
{
MCCategory: "Personal",
MCPhoneNumber: "555-555-5555",
Title: "John E. Doe"
},
{
MCCategory: "Personal",
MCPhoneNumber: "666-666-6666",
Title: "John F. Doe"
}
];
// Log
console.log("Creating the items.");
// Get the list
var list = $REST.List("My Contacts");
// Parse the data
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
// Add the item
list.Items().add(data[i]).execute(true);
}
// Wait for the items to be added
list.done(() => {
// Log
console.log("The items were created.");
});
}
Main (src/index.ts)
The main source will create a global variable and use the SharePoint Script-On-Demand to notify the webpart when the library has been loaded. The initialize method will create an instance of the webpart. If we are displaying the data, then we will render the list view using VueJS.
// Libraries
import { Types } from "gd-sprest";
import { WebParts } from "gd-sprest-js";
import * as Vue from "vue";
// CSS
import "gd-sprest-js/build/lib/css/fabric.min.css";
// Local
import { Configuration } from "./cfg";
/**
* Vue JS Demo
*/
window["VueJSDemo"] = {
// Configuration
Configuration: Configuration,
// Initialize the webpart
init: function () {
// Create an instance of the webpart
WebParts.WPList({
odataQuery: {
OrderBy: ["Title"]
},
cfgElementId: "wp-vuejs-cfg",
elementId: "wp-vuejs",
wpClassName: "fabric",
onRenderItems: function (wpInfo, items) {
/* Render the webpart */
new Vue({
el: wpInfo.el,
data: () => {
return { contacts: items };
},
template: [
'<div class="table">',
'<div class="row" v-for="contact in contacts" :key="contact.Id">',
'<div></div>',
'<div></div>',
'<div></div>',
'</div>',
'</div>'
].join('\n')
});
}
});
}
};
// Let SharePoint know the script has been loaded
SP.SOD.notifyScriptLoadedAndExecuteWaitingJobs("demo-vue.js");
Compiler Configuration Files
Before we are able to compile the files, we need to update the configuration files.
Package (package.json)
Update the “scripts” and the “build” option. This will allow us to type in “npm run build” to compile the code.
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack"
}
WebPack (webpack.config.js)
The webpack configuration file is similar to others I’ve created in the past, but this one required me to set the “alias”.
var path = require('path');
module.exports = {
// File to target
entry: './src/index.js',
// Output
output: {
filename: 'demo-vue.js'
},
// Resolve the file extensions
resolve: {
alias: {
vue: "vue/dist/vue.js"
},
extensions: [".css", ".js", ".vue"]
},
// Module to define what libraries with the compiler
module: {
// Rules
rules: [
// CSS Files
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
{ loader: "style-loader" },
{ loader: "css-loader" }
]
},
// VueJS Files
{
test: /\.vue$/,
// Exclude the npm libraries
exclude: /node_modules/,
// Define the compiler to use
use: [
{
// Compile the vue code to JavaScript
loader: "vue-loader"
}
]
}
]
}
};
Compile the Code
Run ‘npm run build’ or ‘webpack’ to compile the code and create the ‘demo-vue.js’ file located in the dist folder.
Demo
Step 1 - Create Demo Page
1) Upload the file to SharePoint 2) Create a webpart page of your choice 3) Access the page
Step 2 - Install the WebPart
1) Press F-12 to access the developer tools 2) Click on the “Console” tab 3) Reference the script - We will use simple javascript to insert a script link into the page. Afterwards, our library will be available.
var s = document.createElement("script");
s.src = "/sites/dev/siteassets/demo-vue.js";
document.head.appendChild(s);
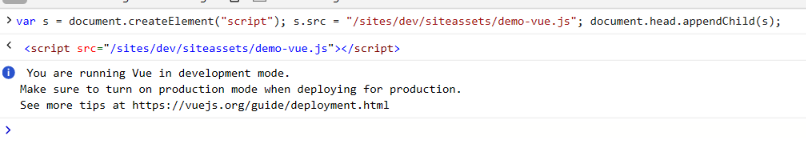 4) Install the list
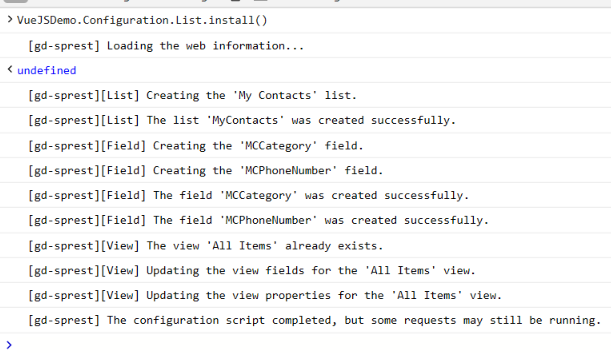
4) Install the list
VueJSDemo.Configuration.List.install()
 5) Add the test data
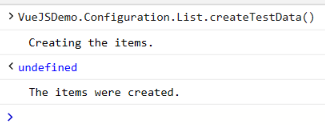
5) Add the test data
VueJSDemo.Configuration.List.createTestData()
 6) Install the webpart
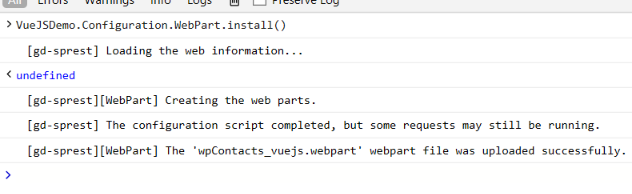
6) Install the webpart
VueJSDemo.Configuration.WebPart.install()
Step 3 - Test
1) Edit the page 2) Click on a webpart zone to add a new webpart 3) From the webpart gallery, select the “Demo” group “My Contacts (VueJS)” webpart  4) After the page reloads, you will see the edit configuration button
4) After the page reloads, you will see the edit configuration button  5) Click on the button to display the configuration panel
5) Click on the button to display the configuration panel  6) Select the ‘My Contacts’ list and save the webpart
6) Select the ‘My Contacts’ list and save the webpart 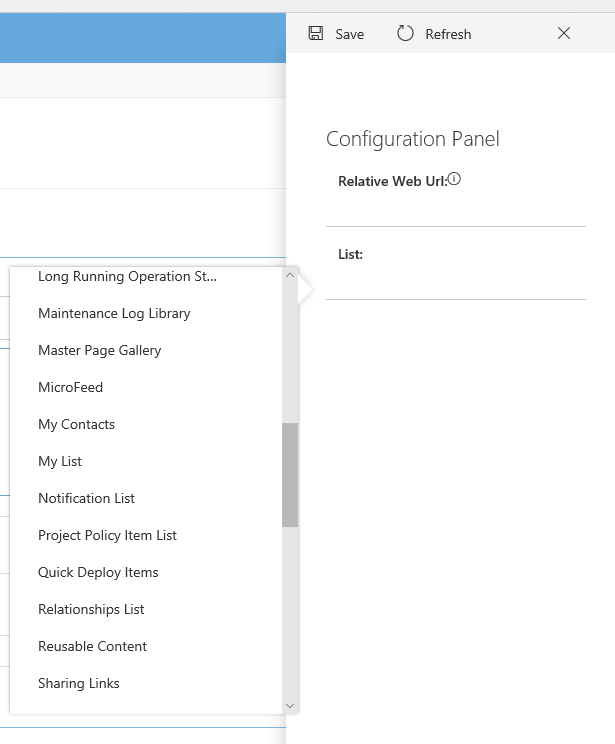 7) Save the page, and when the page reloads you will see the contacts test data
7) Save the page, and when the page reloads you will see the contacts test data 
Step 4 - Clean Up
1) Press F-12 to access the developer tools 2) Click on the “Console” tab 3) Uninstall the list and webpart
VueJSDemo.Configuration.WebPart.uninstall()
This part may take a little time to initialize, depending on the size of the web. 
Output Size
One thing to note, is the output file size (uncompressed) is about 745KB. This is much smaller than the react/fabric-ui demo we just created, but it’s important to note that the react demo also included the Office Fabric UI React library on top of the react library.
Conclusion
I hope this post was useful for using the VueJS framework. In the next post we will explore AngularJS framework.